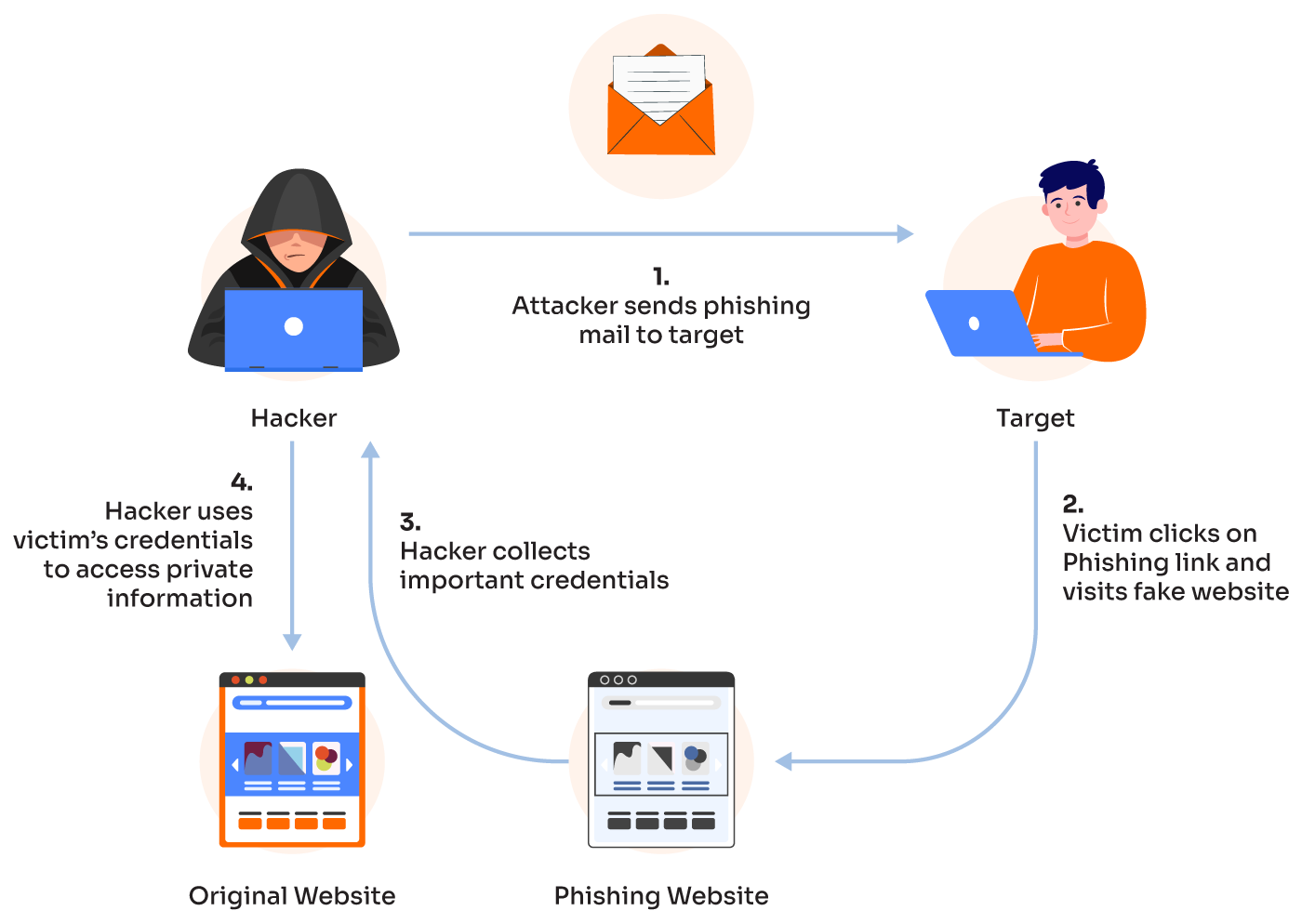
Common Phishing Techniques
Phishing is a method used by hackers to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or financial details. Here’s a list of common phishing techniques and ways to avoid them:
Common Phishing Techniques
- Email Phishing:
- Description: Fraudulent emails that appear to be from legitimate organizations (banks, tech companies) requesting personal information.
- Avoidance:
- Verify the sender’s email address.
- Look for spelling and grammatical errors.
- Never click on links or download attachments from unknown senders.
- Spear Phishing:
- Description: Targeted phishing aimed at specific individuals or organizations, often using personal information to appear legitimate.
- Avoidance:
- Be cautious about sharing personal information online.
- Verify any requests for sensitive information through official channels.
- Whaling:
- Description: A type of spear phishing targeting high-profile individuals (CEOs, executives) within an organization.
- Avoidance:
- Educate executives about phishing tactics.
- Implement strict verification processes for financial transactions.
- Smishing:
- Description: Phishing via SMS text messages, often containing links to malicious sites or requesting personal information.
- Avoidance:
- Don’t click on links in unsolicited messages.
- Verify the sender before responding.
- Vishing:
- Description: Voice phishing, where attackers use phone calls to trick individuals into providing sensitive information.
- Avoidance:
- Don’t share personal information over the phone unless you’re sure of the caller’s identity.
- Hang up and call back using official contact numbers.
- Clone Phishing:
- Description: An attacker creates a nearly identical copy of a legitimate email that has previously been sent, altering it to include a malicious link or attachment.
- Avoidance:
- Check for discrepancies in the email content, especially if you receive a follow-up message.
- Use email security tools to detect cloned messages.
- Website Spoofing:
- Description: Attackers create fake websites that closely mimic legitimate ones to collect login credentials or personal information.
- Avoidance:
- Always check the URL for legitimacy (look for HTTPS and correct domain names).
- Use bookmarks to access important sites instead of clicking on links.
- Malware-based Phishing:
- Description: Attackers use malware to infect a device and capture sensitive information without the victim’s knowledge.
- Avoidance:
- Use updated antivirus software.
- Avoid downloading software or files from unknown sources.
General Prevention Strategies
- Education and Awareness: Regularly train employees and individuals on recognizing phishing attempts and safe online practices.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security even if credentials are compromised.
- Email Filters: Use spam filters and email security solutions to detect and block phishing attempts.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a plan in place for responding to suspected phishing attempts, including reporting procedures.
By staying informed and vigilant, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks.
Leave a Reply